Tortoises are among the longest-living creatures on Earth, known for their slow pace and remarkable longevity. Understanding the Tortoise Life Period helps owners, wildlife enthusiasts, and researchers care for these reptiles more effectively. In this article, we explore how long tortoises live, the factors that influence their lifespan, differences among species, and practical tips to extend their life.
Understanding the Tortoise Life Period
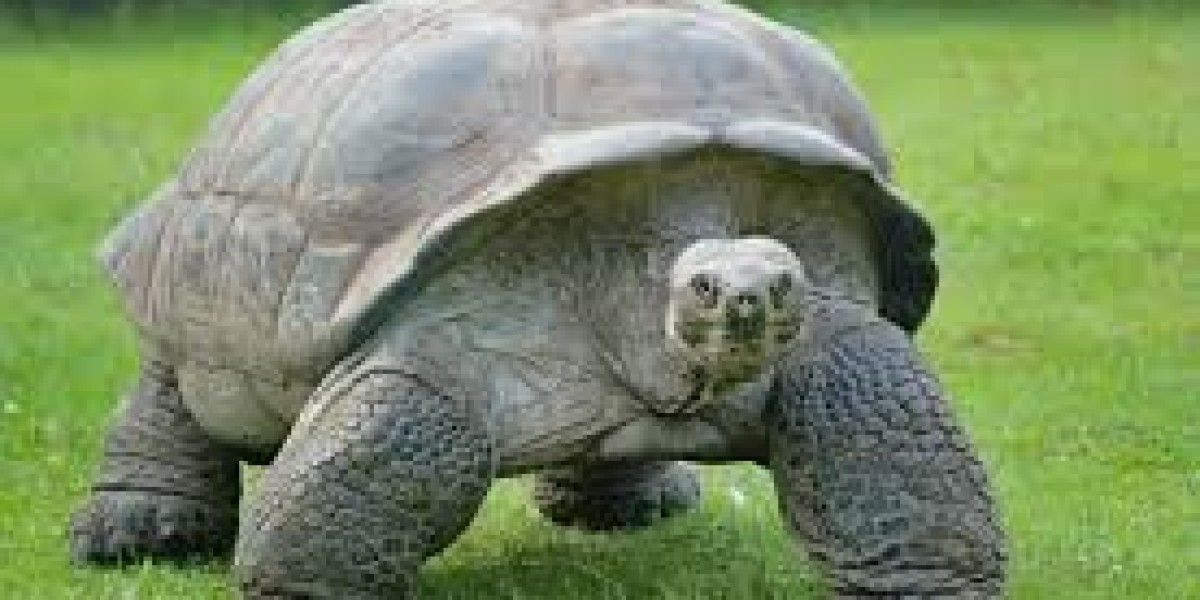
The Tortoise Life Period refers to the average number of years a tortoise can live in its natural environment or captivity. Lifespans can vary greatly depending on species, diet, habitat, and healthcare. Many tortoises live well over 50 years, with some species, like the Galapagos tortoise, surpassing 100 years.
Knowing the Tortoise Life Period is crucial for potential owners or caretakers because it represents a long-term commitment. Proper understanding ensures that tortoises are provided with suitable housing, nutrition, and medical care throughout their lives.
Tortoise Life Period: How Long Do They Really Live?
The actual lifespan of a tortoise depends on several factors, including genetics, diet, and environment. For example, common pet species like the Russian tortoise may live between 40 and 50 years, whereas larger species like the Aldabra giant tortoise can reach 80 to 150 years in optimal conditions.
In the wild, predation and environmental hazards can reduce their lifespan. In captivity, tortoises often live longer due to controlled conditions, regular feeding, and protection from predators. Understanding the difference between wild and captive Tortoise Life Period helps caretakers provide the best care possible.
Factors Affecting the Tortoise Life Period
Several factors influence the Tortoise Life Period, and being aware of them is essential for maintaining healthy tortoises:
Diet – Proper nutrition rich in fiber, calcium, and vitamins supports longevity.
Habitat – Adequate space, temperature control, and shelter are vital.
Health Care – Routine check-ups, parasite control, and injury care extend life.
Stress – Minimal handling and a safe environment reduce stress-related issues.
For reliable advice, many tortoise enthusiasts consult experts like park hills animal Hospital for guidance on diet, enclosure setup, and long-term health management.
Lifespan of Popular Tortoise Species
Different tortoise species have distinct Tortoise Life Periods:
Russian Tortoise: 40–50 years
Sulcata Tortoise: 50–70 years
Aldabra Giant Tortoise: 80–150 years
Galapagos Tortoise: 100–200 years
Smaller tortoises tend to have shorter lifespans, while giant species are among the longest-living reptiles. Knowing these differences allows owners to make informed decisions when selecting a species.
Environmental Factors That Influence Tortoise Life Period
Environmental conditions play a major role in determining a tortoise’s longevity. Factors like climate, humidity, exposure to sunlight, and availability of clean water can significantly affect health. Tortoises kept in outdoor enclosures need protection from extreme temperatures, predators, and diseases to maintain their Tortoise Life Period.
Proper habitat design, including UVB lighting for indoor tortoises, is essential for bone and shell health. A well-maintained environment directly contributes to longevity and quality of life.
Common Health Issues Affecting Tortoise Life Period
Several health problems can reduce the Tortoise Life Period if not addressed promptly. These include:
Respiratory infections from poor ventilation
Shell rot caused by excessive moisture
Metabolic bone disease from calcium deficiencies
Parasite infestations
Routine veterinary care and preventive measures are critical. Consulting experienced professionals, such as those at park hills animal, ensures early detection and treatment of health issues that may shorten lifespan.
Tips to Extend the Tortoise Life Period
Owners can take several steps to maximize their tortoise’s longevity:
Provide a balanced diet – Leafy greens, vegetables, and calcium supplements.
Maintain a suitable habitat – Proper temperature, UVB lighting, and safe space.
Regular health check-ups – Early detection of diseases or deficiencies.
Minimize stress – Limit handling and create a quiet, safe environment.
Hydration – Regular access to clean water for drinking and soaking.
By following these guidelines, tortoise owners can help ensure their pet reaches or even exceeds its expected Tortoise Life Period.
Final Thoughts
The Tortoise Life Period is impressively long compared to most pets, requiring careful planning and lifelong commitment. Understanding species-specific lifespans, environmental needs, diet, and health care is essential for ensuring tortoises live full, healthy lives. With proper care, attention, and expert guidance from professionals like park hills animal, tortoises can thrive and remain a joy for generations to come.