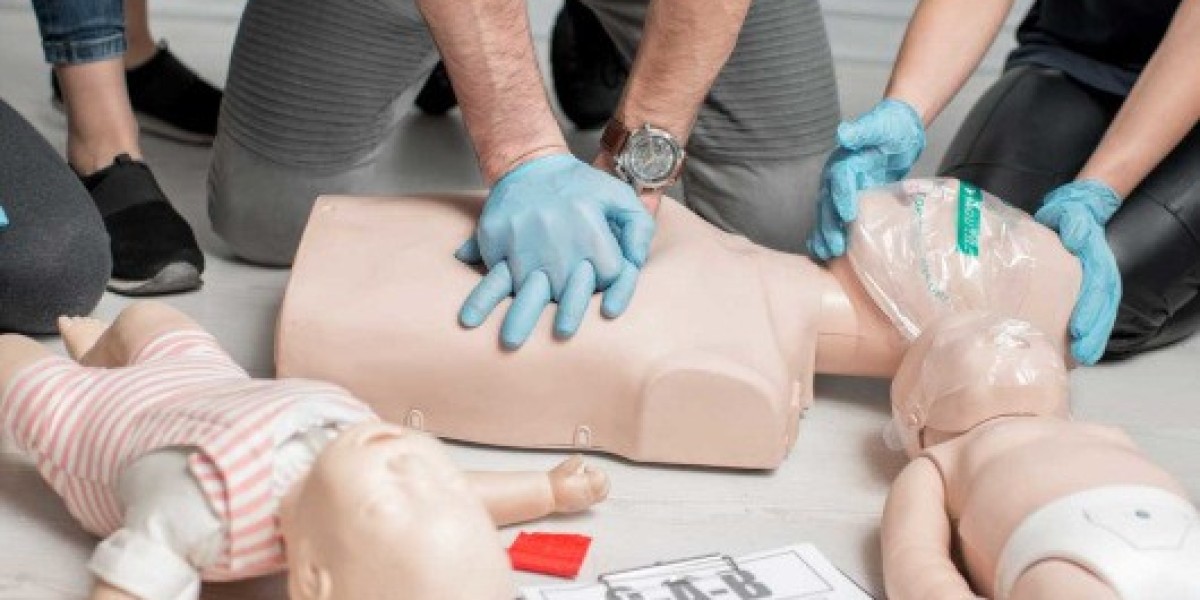
Responding effectively during an emergency can make the difference between life and death. While basic first aid provides foundational skills, many real-world situations require a higher level of knowledge and confidence. That’s where advanced first aid comes in—offering individuals the capability to manage complex injuries, stabilise patients, and support emergency services until professional help arrives. Whether at work, in the community, or on the road, being equipped with advanced emergency response skills empowers people to act decisively when every second counts.
Why Advanced Emergency Skills Matter
Emergencies don’t always follow predictable patterns. Severe trauma, sudden medical episodes, remote-area incidents, and high-risk environments require more than basic bandaging or CPR abilities. Individuals trained in advanced care can assess situations more thoroughly and provide higher-level interventions that greatly improve patient outcomes.
In industries such as construction, manufacturing, education, hospitality, and transport, trained responders are often the first on scene. Their ability to perform structured assessments, control severe bleeding, manage fractures, or assist someone suffering from shock can significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications. The more skilled a responder is, the safer the overall environment becomes.
Key Components of Advanced First Aid Training
Advanced training goes beyond entry-level techniques. It equips participants with a deeper understanding of physiology, risk management, and emergency procedure. Here are the core competencies typically included:
1. Comprehensive Patient Assessment
Responders learn how to conduct systematic primary and secondary assessments, identify hidden injuries, and monitor changes in patient condition. This skill ensures that life-threatening issues are prioritised and addressed.
2. Airway and Breathing Management
Advanced courses cover techniques such as airway adjuncts, oxygen administration, and the management of respiratory distress. These interventions are critical when dealing with asthma attacks, allergic reactions, or traumatic injuries.
3. Bleeding Control and Shock Management
Severe bleeding is one of the most time-sensitive emergencies. Participants learn tourniquet application, wound packing, pressure bandaging, and how to recognise and treat different types of shock.
4. Trauma and Musculoskeletal Injuries
Training includes splinting fractures, immobilising spinal injuries, and managing burns, crush injuries, and heavy impacts. These skills are essential in workplaces or environments where physical injury is common.
5. Medical Emergencies
From diabetic complications to seizures, strokes, and cardiac events, responders learn how to identify symptoms quickly and stabilise patients while awaiting medical support.
6. Environmental and Remote-Area Response
In some cases, professional help may be delayed due to location. Advanced training provides guidance for managing heatstroke, hypothermia, dehydration, and bites or stings—especially important for outdoor workers or recreational groups.
7. Communication and Incident Reporting
Clear, concise communication ensures smooth coordination with emergency services. Trainees learn how to document incidents, relay patient information, and support broader safety protocols.
Who Should Undertake Advanced Training?
While anyone can benefit, this level of training is especially valuable for:
Workplace safety officers
Teachers and childcare professionals
Sports coaches and fitness trainers
Hospitality and tourism staff
Security personnel
Community group leaders
Outdoor guides and remote-area workers
Parents, caregivers, and community volunteers also gain peace of mind from knowing they can act effectively when needed.
The Role of Training Providers
A quality program ensures participants receive hands-on practice, real-world scenarios, and clear guidance from experienced instructors. Providers such as Growth Training Group deliver comprehensive, nationally recognised courses designed to build genuine confidence—not just theoretical knowledge. Choosing a reputable organisation ensures learners receive up-to-date techniques aligned with industry standards and emergency response best practices.
Advanced First Aid in the Workplace
Businesses have a responsibility to provide a safe environment for employees and visitors. Having trained responders on-site reduces risk, supports compliance, and contributes to a culture of safety. Many workplaces choose to upskill key staff to handle multiple emergency types, particularly if they operate in high-risk sectors.
Regular training refreshers keep skills sharp and ensure staff members remain prepared for unexpected incidents. When emergencies occur, the goal is always the same: protect life, reduce harm, and maintain control until professionals take over.
Practical Tips for Responders
Even after completing training, responders can follow certain practices to stay ready:
Review emergency procedures regularly
Keep a well-stocked first aid kit and know its contents
Update CPR and first aid certifications as required
Participate in drills or simulated scenarios
Stay calm, focused, and systematic during real emergencies
Preparation plays a significant role in effective response.
Conclusion
Emergencies can be overwhelming, but the right knowledge transforms uncertainty into decisive action. Developing skills in advanced first aid enables individuals to manage complex situations, provide life-saving interventions, and support others when they need it most. Whether at home, at work, or in the community, investing in advanced training means being ready for the unexpected—and capable of making a profound difference.